Causes of World War One
Here is a map of Europe in 1900. Note the differences from today:
Download the pdf from the Edublog page entitled: The Moroccan Crises and the Balkan Wars.
For both of the Moroccan Crises and both of the Balkan Wars they need to make notes on what happened, when it happened, where it happened, who was involved, why it happened and why it was important as a cause of the first world war.
Origins of the First World War
Read the following views of Historians about the origins of the first world war:
This article has some excellent ideas that you can use in your work and will also deepen your understanding of the causes of World War One:
http://takimag.com/article/world_war_i_taki/print#axzz2pyllgazm
Here are 10 current historians discussing who was to blame for WW1:
http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/magazine-26048324
Peel the Fruit
This Thinking Routine is designed to help you uncover complexity. It will help you to connect what we have learned so far and to get the root cause of why the First World War started.
Begin on the outside with the facts and gradually work to the inside building complexity as you go. Down load the pdf below for full instructions:
The Practice of the First World War
Overview of the war on the Western Front
http://www.firstworldwar.com/battles/sea.htm
http://www.contentextra.com/bacconline/bacContentFiles/histWarsFiles/Historypdfs/Worksheet_33.pdfThe Ludendorff Offensive 1918:
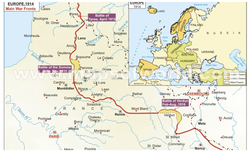
The Western Front
Use this extract from the textbook and the internet links to help
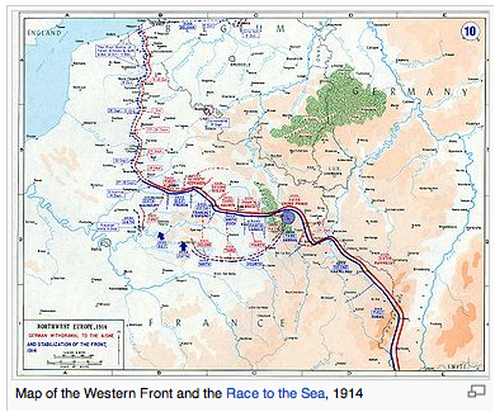
The Creation of the Western FrontFind out:
1. Where was the Western Front? Why is it called ‘Western’ and what is a front?
2. How long was the Western Front?
3. What was the Race to the Sea?
4. Why didn’t the Western Front move very much for the whole war, 1914 – 18?
http://www.johndclare.net/wwi1.htm
http://www.the-map-as-history.com/maps/6-first-world-war.php
YOUR TASK:
How was the war fought on land?
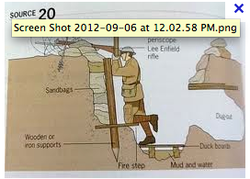
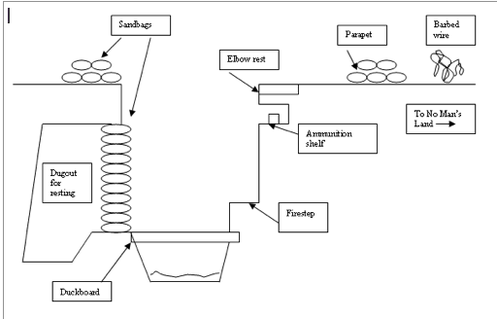
1. Trenchwarfare:What is a trench?
http://www.bbc.co.uk/programmes/p022twsy
1. How did trench warfare work?
2. Why did trench warfare lead to so many deaths?
3. How did trench warfare combined with the machine gun lead to a stalemate?Here are some extracts from the textbook:
Trench warfare
Battle of the Somme
2. New Weapons
The Battle of the Somme July 1st 1916
http://www.spartacus.schoolnet.co.uk/FWWsomme.htm
Read the information below and make a list of the new weapons that were developed. How successful were the weapons? What was the impact of the weapons on the fighting and the tactics?
Life in the Trenches
How was the war fought at Sea?
http://www.firstworldwar.com/battles/sea.htm
http://www.bbc.co.uk/history/worldwars/wwone/war_sea_gallery.shtml
4. The Eastern Front
Read these two pieces of information about the Eastern Front using the thinking strategy: Connect – Extend – Challenge
This is an amazing article about the White War between Italy and Austria -Hungary:
5. Why did the Central Powers lose the first world war? Why did the USA enter the war in 1917?
* Who were the Central Powers?
* What happened in 1917 in Russia and in the USA?
* What was the Ludendorff Offensive?
Now consider the question using the Thinking Strategy: Claim – Support – Question by making a mind map using three colours
You have a choice of essay titles. Either write about why the USA entered the war or why the Central Powers lost the war.
Here is a student essay which answers this question. It scored a 7:
Analyse the factors that led to the defeat of the Central Powers in World War One.
6. In what ways was the First World War a Total War?
Define the term “total war”.
Complete the mind map on page 61 of the reading below to show the ways in which the first world war was a total war. For each aspect of the mind map give a clear example or include reference to an Historian who supports this view.
7. Effects of the War
This is an amazing article about the White War between Italy and Austria -Hungary:
Inventions that were inspired by the first world war:
http://www.bbc.com/news/magazine-26935867
7. Historiography
The link below has summarised many of the views of the main Historians who write about the first world war.
http://www.pbs.org/greatwar/historian/index.html