The aim of this section is to be able to discuss the reasons for and consequences of the relocation of polluting industries [such as the e-waste recycling industry] and waste disposal [e-waste] to countries with weaker environmental controls and safety regulations.
Read this story from The Guardian about the issue of mobile phone waste and how manufacturers like Apple & Samsung are being encouraged to take a more sustainable approach.
Designed for the dump:
Historical examples illustrating how the globalisation of industry allows exploitation of different laws (e.g. environmental) include the 1984 Union Carbide accident in Bhopal, and the Trafigura incident 2006.
E-waste
e-waste in Ghana – geography education.org
Agbogbloshie – Ghana’s e-waste town (Wikipedia)
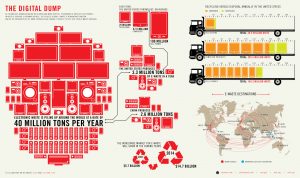
Where does e-waste go?
Focus on China
Guiyu – China’s e-waste town (Wikipedia)
Unused e-waste discarded in China raises questions 2012 BBC
Case study – Rare Earth metals, Baotou, Inner Mongolia
NASA images showing impact of mining and processing rare earth metals
Daily Mail – Rare earth metals used in wind turbine generators
The Guardian – Rare Earth metals from China – Environmental consequences
China cuts back on accepting international consumer waste
CNN – China refuses to recycle more of the world’s trash
Guardian – Moment of reckoning: US cities burn recyclables after China bans imports (Feb 2019)
Possible question
“Polluting industries are relocated away from developed nations, for purely financial reasons.” Discuss this statement [15 marks]