Paper 2: (HL/SL) Authoritarian and Single Party States
Paper 2: (HL/SL) Democratic States – challenges and responses
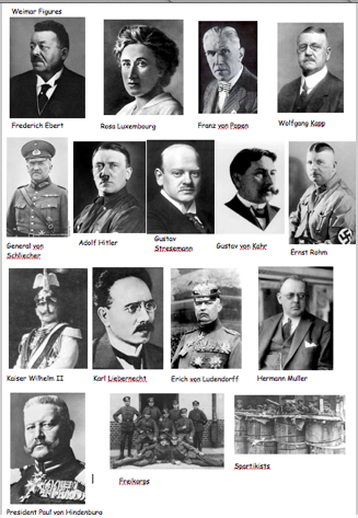
1. What do we already know about Germany after World War One?
Watch the movie Make Germany Pay to review the Peace Conferences and introduce the difficulties faced by Germany after 1919.
2. How and why was the Weimar Republic created in 1918?
With a partner discuss what you already know about the set up of the Weimar Republic. Link to the end of World War One. Complete the first five pages of the worksheet below using the white books to help if you need them:
The Weimar Republic worksheet
3. What problems did the Weimar Republic face between 1918 and 1923?
* Constitution
* Putsches and Uprisings
* Hyper Inflation
* Ruhr Crisis
Problems faced by the Weimar Republic
Life in the Weimar Republic during the Great Inflation
The reparation payments were finally paid in 2010:
Final reparation payments
4. How did the Weimar Republic Survive after 1923?Who was Gustav Stresemann and what was the ‘Stresemann Era’? How did the Great Depression affect Germany? |
|
6. Opinions of the Weimar Republic
“Internal political extremism was the main challenge to democracy in the twentieth century.”
With reference to one democratic state, to what extent do you agree with this statement?
Complete an essay scaffold to answer this question.
Perspective (Grade 11)
What different perspectives of the Weimar Republic can you identify?
What views would these groups have?
Who was Adolf Hitler?Create a biography of Adolf Hitler on one side of A3 using a Pages template.
Include the following: *A Photo of Hitler *Key points about: childhood and family, life before the first world war, experience during the first world war, first political experiences, Munich Putsch, time in prison up to 1924. BULLET POINTS ONLY *Images or pictures to communicate Hitler’s background
*No information after 1924.
*Submit to drop box
|
Hitler in Vienna 1913 (with Trotsky, Stalin, Freud and Tito)To read more about how these famous men lived in Vienna at the same time use this link: Vienna 1913
|
Hitler’s Ideology
Hitler’s ideology from; Todd, Alan and Waller, Sally. (2011) Authoritarian and Single Party States. UK: Cambridge
Hitler’s Rise to Power
Connect – Extend – Challenge
Read the pdf below about Hitler’s Rise to Power and write your Connections and Extensions:
Think about:
What methods did Hitler use to secure power in 1933?
|
Hitler’s consolidation of power
Consolidation of Power
Eight steps to becoming a dictator
The Nazi Revolution

- Find out what the problem was
- Find out what Hitler was aiming at (hint: ideology)
- Find out what Hitler did
- Decide if it was successful by comparing the data to the aims.
Opposition to the Youth Policy
Opposition to the Women policy
Opposition to Nazi religious policy
Hitler’s Foreign Policy

Aims in foreign policy
How did Hitler destroy the Treaty of Versailles?
Why did Hitler sign the Nazi Soviet Pact in August 1939?
The Holocaust
Look at the timeline of the Holocaust below. With a partner discuss how it can be divided into three sections – discrimination, persecution and extermination.
Timeline of the Holocaust
Who was responsible for the Holocaust?
How could the Holocaust happen?
Lithuania Holocaust Article:
http://edition.cnn.com/2010/WORLD/europe/06/03/lithuania.nazi.prosecutions/index.html?hpt=C1
Historiography
This BBC In Our Time podcast includes an interview with Ian Kershaw and discusses the different theories of Historiography surrounding Hitler:
This is a summary of Historian’s views from johndclare:
Propaganda
Nazi propaganda posters
Hitler’s idea of the People’s Car was a huge success but was not mass produced until after the Second World War:
http://www.bbc.com/culture/story/20130830-the-nazi-car-we-came-to-love